Abstract
Background: For patients (pts) with intermediate or high risk myelofibrosis (MF) who have failed or are intolerant to JAK inhibitors such as ruxolitinib, there are no standard therapies. Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac) mimetics lead to increased apoptotic cancer cell death, especially in high TNFα-expressing tumor models, and significantly increased levels of TNFα in pts with MF has been demonstrated (Fleischman AG, Blood 2011). LCL161 was previously investigated in pts with advanced solid tumors (Infante JR, J Clin Oncol 2014); the current clinical trial is the first-in-myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) pt study.
Objectives: Primary: to determine efficacy (IWG-MRT 2013) of LCL161 for pts with MF. Secondary: to determine change in symptom burden (MPN-Total Symptom Score). Exploratory: detection for non-driver molecular mutations via next generation sequencing and assessment of markers of IAP protein degradation.
Methods: We are conducting an investigator-initiated, single-center, phase 2 study of LCL161 for pts with MF in a Simon's two-stage design. Pts age ≥18, PS=0-2, intermediate to high risk MF, who are intolerant to, ineligible for, or relapsed/refractory to JAK inhibitors are eligible. There is no threshold requirement for spleen size or platelet (plt) count; pts with prior allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) are also eligible. LCL161, an oral (po) drug, was administered at starting dose 1500mg po once weekly. Each cycle=28 days. Initial protocol response assessments are performed at 3 months, then every 3 months thereafter.
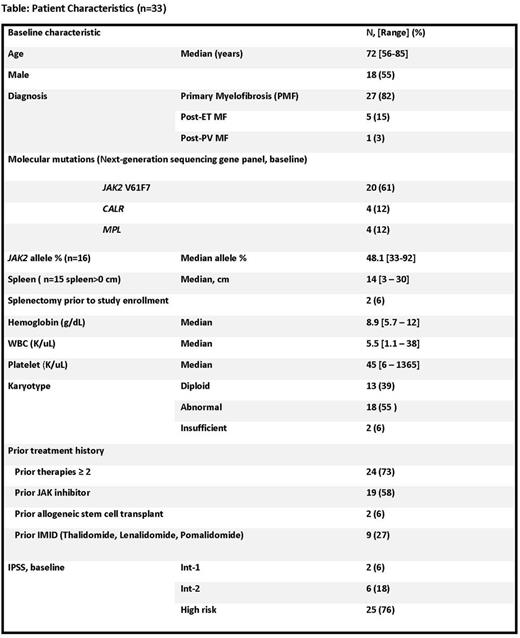
Results: From January 2015 to July 2017, 33 pts have been enrolled. Baseline pt characteristics are listed in Table. JAK2 V617F mutation occurred in 20(61%), CALR mutation in 4(12%), and MPLW 515L mutation in 4(12%) pts. 5 pts were "triple negative" (negative for JAK2, CALR, MPL). The most common non-driver molecular mutations were: TET2 (n=5); DNMT3A (n=4); ASXL1 (n=4); RAS (n=2); EZH2 (n=1). 24 (73%) had ≥2 prior therapies. 2 pts had prior SCT. By IPSS, 25(76%) were high risk MF. Median number of cycles received=4 [1-31+], median treatment duration=4.2 months [0.9-28.6+]. 24 pts are alive, with median follow-up of 14 months [0.9-2.6]. Among 30 evaluable pts (3 pts still too early to assess), 9 pts had 13 objective responses (4 pts: 2 separate IWG-MRT 2013 response categories): Clinical improvement (CI) (anemia) in 5 pts; CI (Symptom) in 6 pts; CI (Spleen) in 1 pt; CR (Cyto) in 1pt. 7 of 9 (78%) responders achieved response by 3 months. For all 9 responders, median time to response: 1.8 months [0.9 - 5.5]; median response duration: 12.2 months [2.8-27.7+] Grade 3/4 non-hematologic adverse events: syncope, n=2 (possibly related). No pts had cytokine release syndrome. Most common grade 1/2 non-hematologic toxicities: fatigue (n=19), nausea (n=16), dizziness/vertigo (n=12). Dose reductions: n=10: 7 reduced to dose -1 level (1200 mg po once weekly); 3 reduced to dose -2 (900 mg po once weekly); most common reason for dose reduction: grade 2 fatigue (n=7). 20 pts are now off study [n=9 no response; n=3 toxicity; n=3 transformation to AML; n=2 PD (spleen); n=1 pt request; n=1 due to concurrent condition-chronic liver disease]; and n=1 proceeded to SCT. Updated clinical results will be presented. Ongoing, prospective correlative studies demonstrate on-target inhibition (by Western blot) of CIAP1 in 8 pts: strong (n=4) or moderate (n=4); among the first 6 clinically responding pts, 4 of 4 of these pts with available samples for analysis demonstrated strong, on-target CIAP1 inhibition.
Conclusions: In a cohort of pts with MF with a median age of 72 years, 76% IPSS high risk, median plt count of 45 at study entry, in whom 73% had received ≥2 prior therapies, we observed an overall response rate of 30% with LCL161 monotherapy. LCL161 represents a potentially novel treatment for pts with MPNs, has a convenient (po, weekly) dosing schedule, and is able to be administered to pts who have failed or intolerant/ineligible for JAK inhibitor therapy. Notably, grade 2 fatigue was common, and represents the most common reason for dose reduction and study discontinuation. Future directions may include investigating rational therapies to combine with LCL161, such as hypomethylator therapy (Carter BZ, J Natl Cancer Inst 2014) or chemotherapy (Lueck SC, Oncotarget 2016) in an expanded group of myeloid malignancies. This clinical trial is registered as NCT02098161.
Pemmaraju: novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; cellectis: Research Funding; stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; LFB: Consultancy, Honoraria; roche diagnostics: Consultancy, Honoraria; affymetrix: Research Funding; abbvie: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria. Carter: novartis: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding. Kantarjian: ARIAD: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding. Bose: Incyte Corporation: Honoraria. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. DiNardo: Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding. Daver: Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Immunogen: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding. Cortes: Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding. Verstovsek: NS Pharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal